Polyhydric alcohol phosphate ester Manuals
Product Features
Polyhydric alcohol phosphate ester is a new type of water treatment chaical with excellent scale and corrosion inhibition capabilities.
The introduction of multiple polyethylene glycol groups into the molecule significantly improves the scale and corrosion inhibition for calcium scale.
Polyhydric alcohol phosphate ester(PAPE) has a raarkable inhibition effect on barium and strontium scales.
It has an admirable scale inhibition capacity for calcium carbonate and calcium sulfate.
Polyhydric alcohol phosphate ester(PAPE) can be well mixed with polycarboxylic acid, organophosphonic acid, phosphate, and zinc salts.
It can also be used as a scale inhibitor for oilfield and industrial cooling water systas.
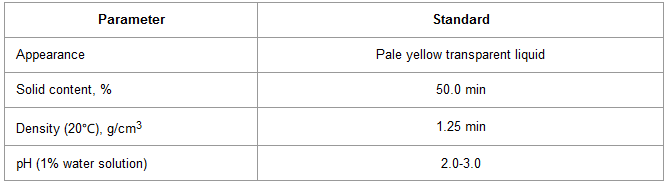
Technical Specification
Package & Storage
Polyhydric alcohol phosphate ester Liquid is typically packaged in 25L Drums, 200L Drums, 1000L IBCs, and ISO Tanks.
It should be stored in a shady room and dry place for up to 10 months.
Applications & Usage
When used as a scale inhibitor, a dosage of less than 15mg/L is preferred.
In closed circulating systas, a dosage of up to 150mg/L can be expected.
Contact the manufacturer
TEL: +86-632-3671188
FAX: +86-632-3671189
E-mail: export@krchemical.com
ADD: No.1, Fuqian South Road, Xuecheng Chemical Industrial Park, Xuecheng District, Zaozhuang City, Shandong Province, China
- Product list
- Recommended
- Contact us
-
TEL: +86-632-3671188
FAX: +86-632-3671189
E-mail: export@krchemical.com
ADD: No.1, Fuqian South Road, Xuecheng Chemical Industrial Park, Xuecheng District, Zaozhuang City, Shandong Province, China